Borealis is a remote management platform with a simple, visual automation layer, enabling you to leverage scripts and advanced nodegraph-based automation workflows. I originally created Borealis to work towards consolidating the core functionality of several standalone automation platforms in my homelab, such as TacticalRMM, Ansible AWX, SemaphoreUI, and a few others.
A Note on Development Pace
I'm the sole maintainer and still learning as I go, while working a full-time IT job. Progress is sporadic, and parts of the codebase get rebuilt when I discover better or more optimized approaches. Thank you for your patience with the slower cadence. Ko-Fi donations are always welcome and help keep me motivated to actively continue development of Borealis.
Features
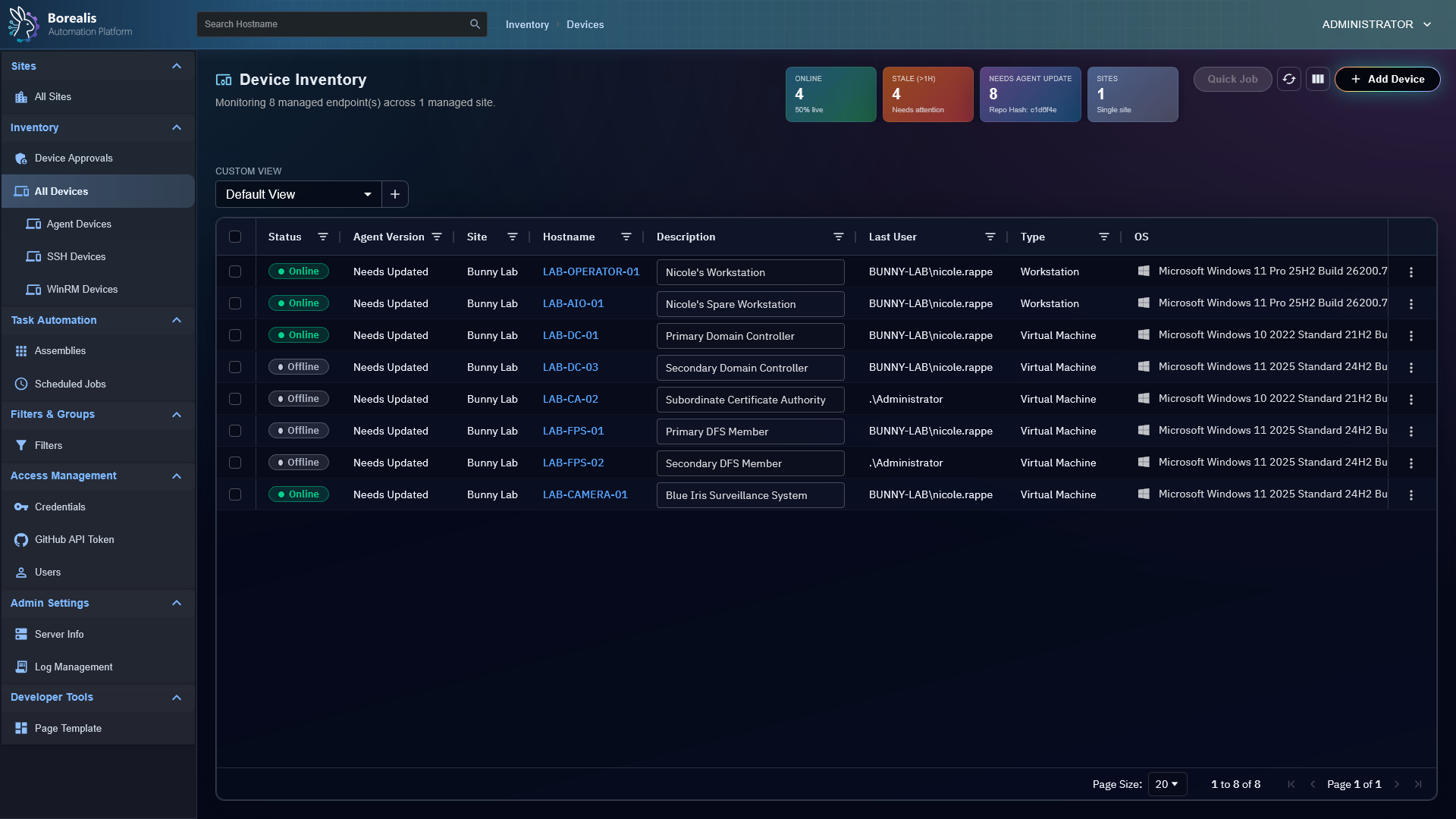
- Device Inventory: OS, hardware, and status posted on connect and periodically.
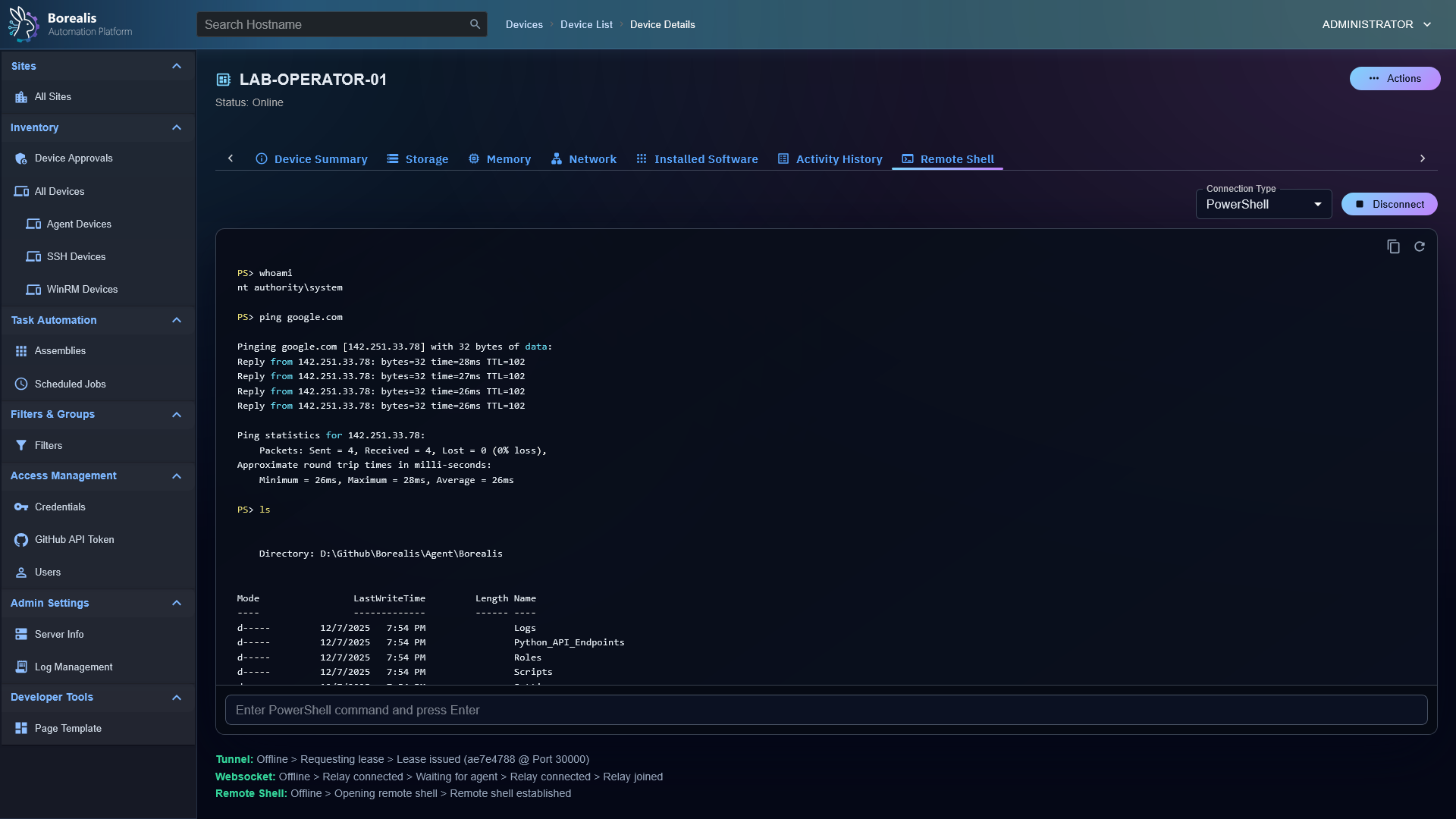
- Remote Script Execution: Run PowerShell in
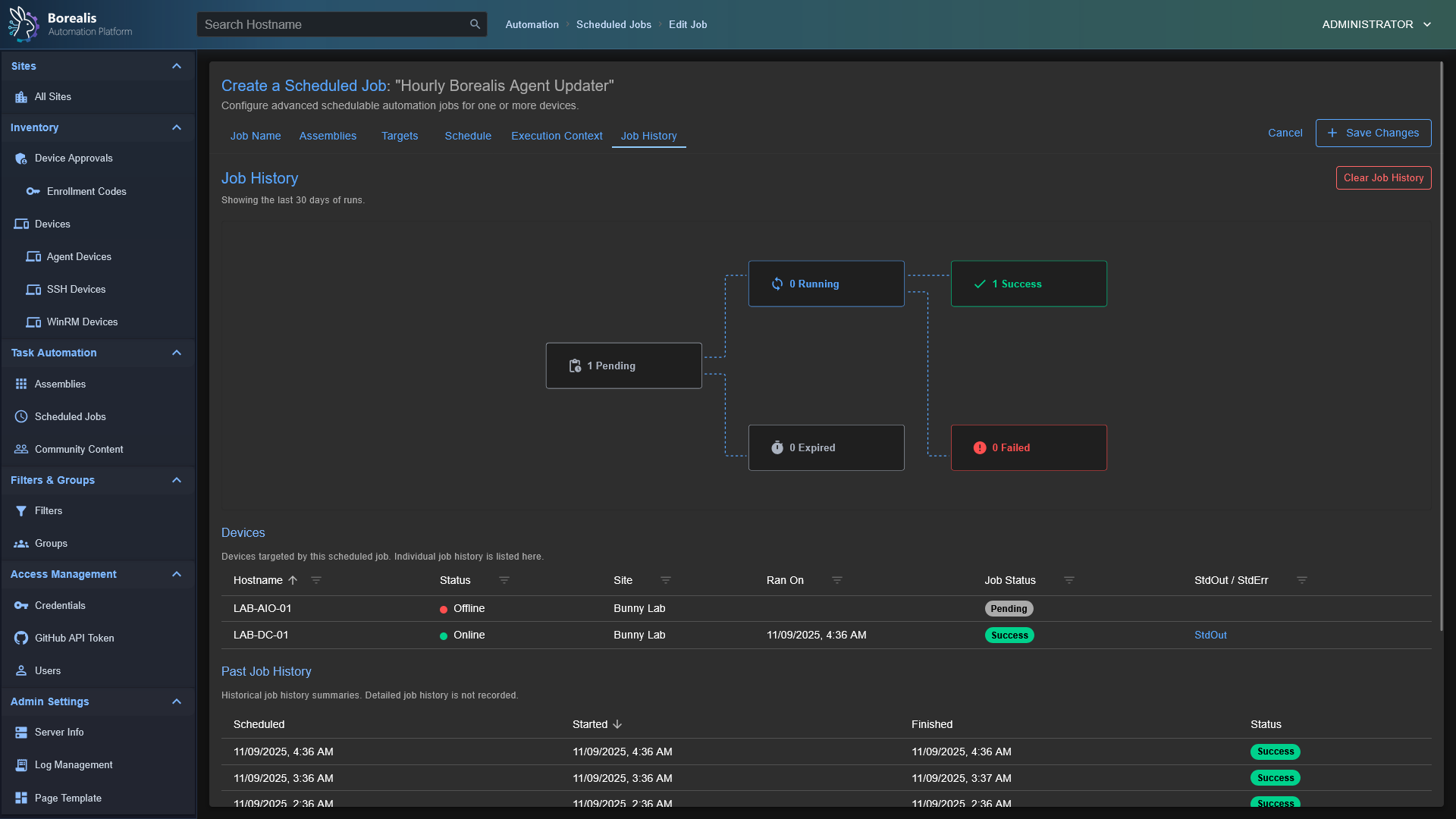
CURRENT USERcontext or asNT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM. - Jobs and Scheduling: Launch "Quick Jobs" instantly or create more advanced schedules.
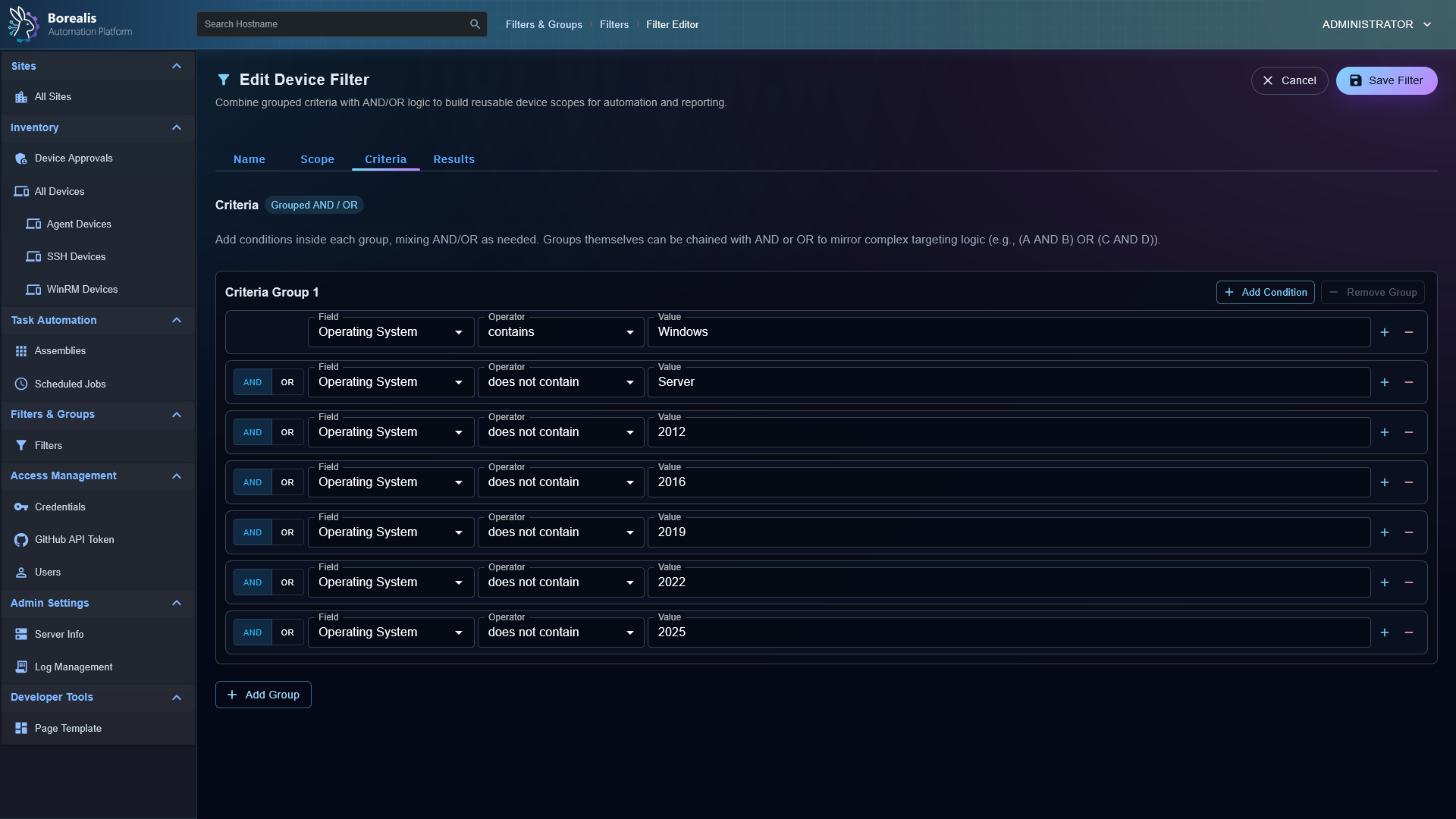
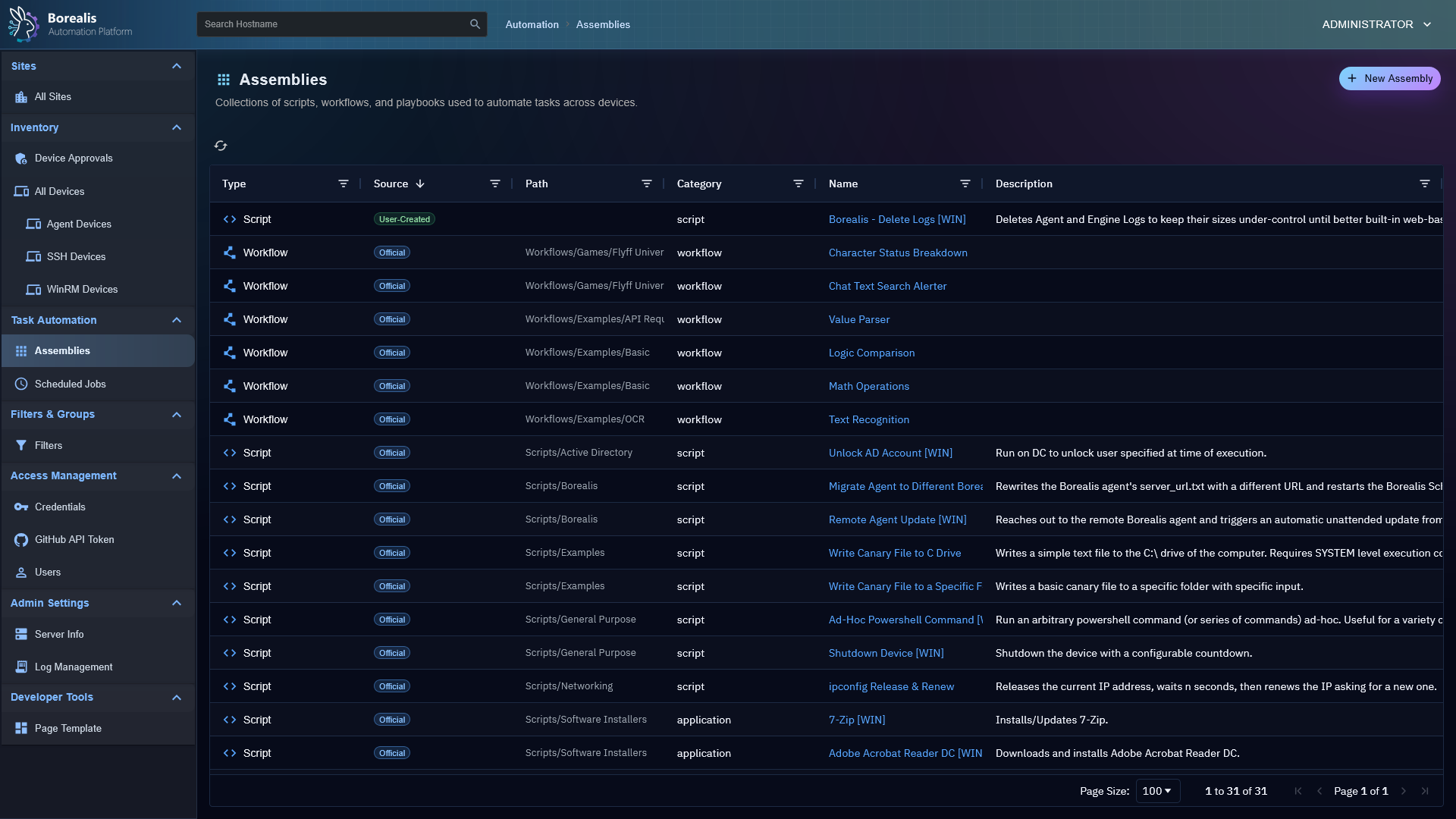
- Visual Workflows: Drag‑and‑drop node canvas for combining steps, analysis, and logic.
- Ansible Playbooks: Ansible playbook support is unfinished/broken in both the Engine and agent runtimes. The goal is to ship server-driven Ansible (SSH/WinRM) alongside agent-driven playbooks.
- Windows‑first. Linux Engine support ships via
Borealis.sh(Engine is currently the focus); the Linux agent is not yet available; only settings can be staged—and the current Linux agent build would not execute scripts, audits, or likely even enroll reliably.
Current Status & Limitations
- Ansible is disabled/unstable: Engine quick-run returns not implemented, scheduled-job and agent paths are incomplete, and server-side SSH/WinRM playbook dispatch is still on the roadmap. Expect failures until the Ansible pipeline is rebuilt.
- Linux agent is non-functional: script execution, auditing, and enrollment flows are Windows-only right now. Avoid Linux agent deployments until a proper port is delivered.
Device Management
Assembly Management
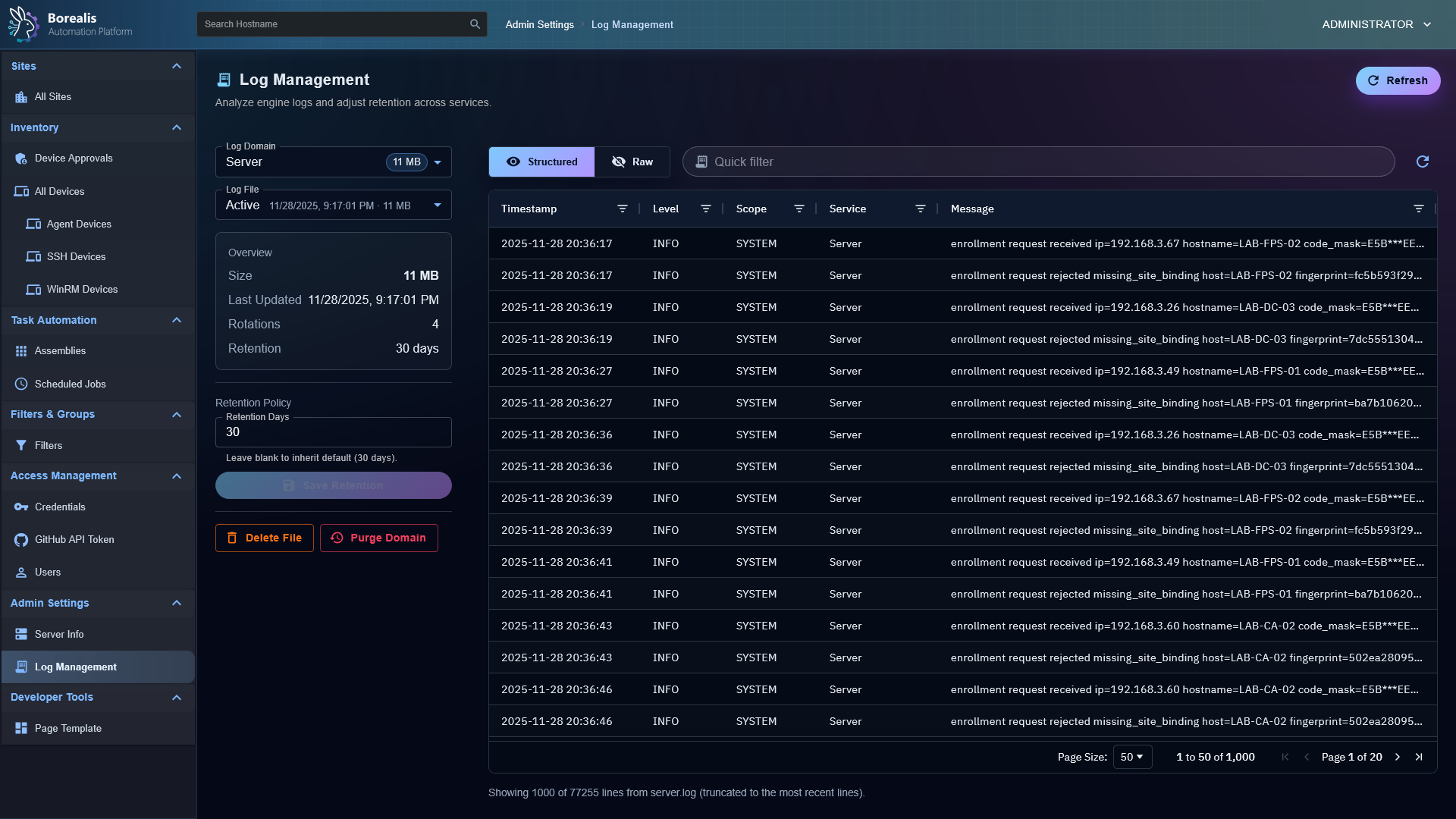
Log Management
Misc Management Sections
Getting Started
Installation
- Start the Engine:
- Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -EngineProductionProduction Engine @ https://localhost:5000 - Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -EngineDevDev (Vite + Flask) @ https://localhost:5173 - Linux (Engine only):
./Borealis.sh --EngineProductionProduction Engine @ https://localhost:5000 (use--EngineDevfor Vite)
- Windows:
- (Optional) Install the Agent (Windows, elevated PowerShell):
- Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -Agent - Linux agent binaries are not available yet;
Borealis.sh --Agentonly stages config settings.
- Windows:
Automated Agent Enrollment
If you plan on deploying the agent via something like a Group Policy or other existing automation platform, you can use the following commandline arguments to install an agent automatically with an enrollment code pre-injected. The enrollment code below is simply an example.
Windows:
.\Borealis.ps1 -Agent -EnrollmentCode "E925-448B-626D-D595-5A0F-FB24-B4D6-6983"
Linux: Agent enrollment is not yet available on Linux; Borealis.sh --Agent only writes settings placeholders.
Reverse Proxy Configuration
Traefik Dynamic Config: Replace Service URL with actual IP of Borealis server
http:
routers:
borealis:
entryPoints:
- websecure
tls:
certResolver: letsencrypt
service: borealis
rule: "Host(`borealis.example.com`) && PathPrefix(`/`)"
middlewares:
- cors-headers
middlewares:
cors-headers:
headers:
accessControlAllowOriginList:
- "*"
accessControlAllowMethods:
- GET
- POST
- OPTIONS
accessControlAllowHeaders:
- Content-Type
- Upgrade
- Connection
accessControlMaxAge: 100
addVaryHeader: true
services:
borealis:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: "http://127.0.0.1:5000"
passHostHeader: true
Security Breakdowns
The process that agents go through when authenticating securely with a Borealis server can be a little complex, so I have included a few sequence diagrams below along with a summary of the (current) security posture of Borealis to go over the core systems so you can visually understand what is going on behind-the-scenes.
Security Overview
Overall
- Borealis enforces mutual trust: each agent presents a unique Ed25519 identity to the server, the server issues EdDSA-signed (Ed25519) access tokens bound to that fingerprint, and both sides pin the generated Borealis root CA.
- End-to-end TLS everywhere: the Engine auto-provisions an ECDSA P-384 root + leaf chain under
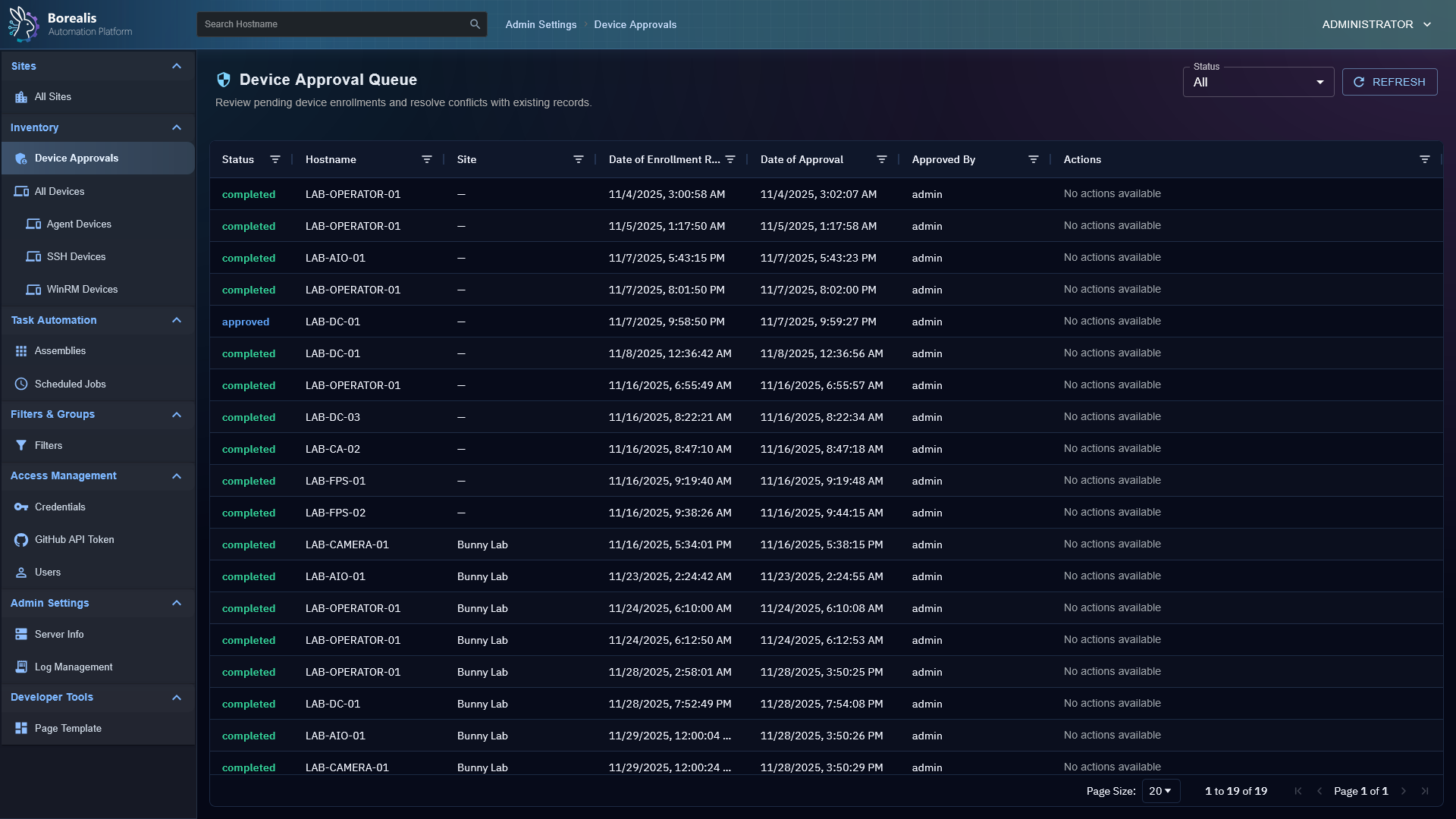
Engine/Certificatesand serves TLS using Python defaults (TLS 1.2+); agents pin the delivered bundle for both REST and WebSocket traffic to eliminate Man-in-the-middle avenues. - Device enrollment is gated by enrollment/installer codes (They have configurable expiration and usage limits) and an operator approval queue; replay-resistant nonces plus rate limits (40 req/min/IP, 12 req/min/fingerprint) prevent brute force or code reuse.
- All device APIs now require Authorization: Bearer headers and a service-context (e.g. SYSTEM or CURRENTUSER) marker; missing, expired, mismatched, or revoked credentials are rejected before any business logic runs. Operator-driven revoking / device quarantining logic is not yet implemented.
- Replay and credential theft defenses layer in DPoP proof validation (thumbprint binding) on the server side and short-lived access tokens (15 min) with 90-day refresh tokens hashed via SHA-256.
- Centralized logging under Engine/Logs and Agent/Logs captures enrollment approvals, rate-limit hits, signature failures, and auth anomalies for post-incident review.
- The Engine’s operator-facing API endpoints (device inventory, assemblies, job history, etc.) require an authenticated operator session or bearer token; unauthenticated requests are rejected with 401/403 responses before any inventory or script metadata is returned and the requesting user is logged with each quick-run dispatch.
Server Security
- Auto-manages PKI: a persistent Borealis root CA (ECDSA SECP384R1) signs leaf certificates that include localhost SANs, tightened filesystem permissions, and a combined bundle for agent identity / cert pinning.
- Script delivery is code-signed with an Ed25519 key stored under Engine/Certificates/Code-Signing; agents refuse any payload whose signature does not match the pinned public key.
- Device authentication checks GUID normalization, SSL fingerprint matches, token version counters, and quarantine flags before admitting requests; missing rows with valid tokens auto-recover into placeholder records to avoid accidental lockouts.
- Refresh tokens are never stored in cleartext, only SHA-256 hashes plus DPoP bindings land in SQLite, and reuse after revocation/expiry returns explicit error codes.
- Enrollment workflow queues approvals, detects hostname/fingerprint conflicts, offers merge/overwrite options, and records auditor identities so trust decisions are traceable.
- Background pruning of expired enrollment codes and refresh tokens is not wired yet; a maintenance task is still needed.
Agent
- Generates device-wide Ed25519 key pairs on first launch, storing them under Certificates/Agent/Identity/ with DPAPI protection on Windows (chmod 600 elsewhere) and persisting the server-issued GUID alongside.
- Stores refresh/access tokens encrypted (DPAPI) and re-enrolls on authentication failures; TLS pinning relies on the stored server certificate bundle rather than a separate fingerprint binding for the tokens.
- Imports the server’s TLS bundle into a dedicated ssl.SSLContext, reuses it for the REST session, and injects it into the Socket.IO engine so WebSockets enjoy the same pinning and hostname checks.
- Treats every script payload as hostile until verified: only Ed25519 signatures from the server are accepted, missing/invalid signatures are logged and dropped, and the trusted signing key is updated only after successful verification between the agent and the server.
- Operates outbound-only; there are no listener ports, and every API/WebSocket call flows through AgentHttpClient.ensure_authenticated, forcing token refresh logic before retrying.
- Logs bootstrap, enrollment, token refresh, and signature events to daily-rotated files under Agent/Logs, giving operators visibility without leaking secrets outside the project root.
Agent/Server Enrollment
sequenceDiagram
participant Operator
participant Server
participant SYS as "SYSTEM Agent"
participant CUR as "CURRENTUSER Agent"
Operator->>Server: Request installer code
Server-->>Operator: Deliver hashed installer code
Note over Operator,Server: Human-controlled code binds enrollment to known device
par TLS Handshake (SYSTEM)
SYS->>Server: Initiate TLS session
Server-->>SYS: Present TLS certificate
and TLS Handshake (CURRENTUSER)
CUR->>Server: Initiate TLS session
Server-->>CUR: Present TLS certificate
end
Note over SYS,Server: Certificate pinning plus CA checks stop MITM
Note over CUR,Server: Pinning also blocks spoofed control planes
SYS->>SYS: Generate Ed25519 identity key pair
Note right of SYS: Private key stored under Certificates/... protected by DPAPI or chmod 600
CUR->>CUR: Generate Ed25519 identity key pair
Note right of CUR: Private key stored in user context and DPAPI-protected
SYS->>Server: Enrollment request (installer code, public key, fingerprint)
CUR->>Server: Enrollment request (installer code, public key, fingerprint)
Server->>Operator: Prompt for enrollment approval
Operator-->>Server: Approve device enrollment
Note over Operator,Server: Manual approval blocks rogue agents
Server-->>SYS: Send enrollment nonce
Server-->>CUR: Send enrollment nonce
SYS->>Server: Return signed nonce to prove key possession
CUR->>Server: Return signed nonce
Note over Server,Operator: Server verifies signatures and records GUID plus key fingerprint
Server->>SYS: Issue GUID, short-lived token, refresh token, server cert, script-signing key
Server->>CUR: Issue GUID, short-lived token, refresh token, server cert, script-signing key
Note over SYS,Server: Agent pins cert, stores GUID, DPAPI-encrypts refresh token
Note over CUR,Server: Agent stores GUID, pins cert, encrypts refresh token
Note over Server,Operator: Database keeps refresh token hash, key fingerprint, audit trail
loop Secure Sessions
SYS->>Server: REST heartbeat and job polling with Bearer token
CUR->>Server: REST heartbeat and WebSocket connect with Bearer token
Server-->>SYS: Provide new access token before expiry
Server-->>CUR: Provide new access token before expiry
SYS->>Server: Refresh request over pinned TLS
CUR->>Server: Refresh request over pinned TLS
end
Server-->>SYS: Deliver script payload plus Ed25519 signature
SYS->>SYS: Verify signature before execution
Server-->>CUR: Deliver script payload plus Ed25519 signature
CUR->>CUR: Verify signature and reject tampered content
Note over SYS,CUR: Signature failure triggers re-enrollment and detailed logging
Note over Server,Operator: Persistent records and approvals sustain long term trust
Code-Signed Remote Script Execution
sequenceDiagram
participant Operator
participant Server
participant SYS as "SYSTEM Agent"
participant CUR as "CURRENTUSER Agent"
Operator->>Server: Upload or author script
Server->>Server: Store script and metadata on-disk
Operator->>Server: Request script execution on a specific device + execution context (NT Authority\SYSTEM or Current-User)
Server->>Server: Load Ed25519 code signing key from secure store
Server->>Server: Sign script hash and execution manifest (The Assembly)
Server->>Server: Enqueue job with signed payload for target agent (SYSTEM or CurrentUser)
Note over Server: Dispatch limited to enrolled agents with valid GUID + tokens
loop Agent job polling (pinned TLS + Bearer token)
SYS->>Server: REST heartbeat and job poll
CUR->>Server: REST heartbeat and job poll
Server-->>SYS: Pending job payloads
Server-->>CUR: Pending job payloads
end
alt SYSTEM context
Server-->>SYS: Script, signature, hash, execution parameters
SYS->>SYS: Verify TLS pinning and token freshness
SYS->>SYS: Verify Ed25519 signature using pinned server key
SYS->>SYS: Recalculate script hash and compare
Note right of SYS: Verification failure stops execution and logs incident
SYS->>SYS: Execute via SYSTEM scheduled-task runner
SYS-->>Server: Return execution status, output, telemetry
else CURRENTUSER context
Server-->>CUR: Script, signature, hash, execution parameters
CUR->>CUR: Verify TLS pinning and token freshness
CUR->>CUR: Verify Ed25519 signature using pinned server key
CUR->>CUR: Recalculate script hash and compare
Note right of CUR: Validation failure stops execution and logs incident
CUR->>CUR: Execute within interactive PowerShell host
CUR-->>Server: Return execution status, output, telemetry
end
Server->>Server: Record results and logs alongside job metadata
Note over SYS,CUR: Pinned TLS, signed payloads, and DPAPI-protected secrets defend against tampering and replay