mirror of
https://github.com/bunny-lab-io/Borealis.git
synced 2026-02-03 21:10:30 -07:00
main
Borealis is a remote management platform with a simple, visual automation layer, enabling you to leverage scripts and advanced nodegraph-based automation workflows. I originally created Borealis to work towards consolidating the core functionality of several standalone automation platforms in my homelab, such as TacticalRMM, Ansible AWX, SemaphoreUI, and a few others.
A Note on Development Pace
I'm the sole maintainer and still learning as I go, while working a full-time IT job. Progress is sporadic, and parts of the codebase get rebuilt when I discover better or more optimized approaches. Thank you for your patience with the slower cadence. Ko-Fi donations are always welcome and help keep me motivated to actively continue development of Borealis.
Documentation
- Human-friendly docs live in
Docs/with a top-level index atDocs/index.md. - The same files also contain Codex Agent sections with deep, agent-focused implementation details.
- Start with
Docs/getting-started.mdandDocs/architecture-overview.md, then jump to the domain pages.
Features
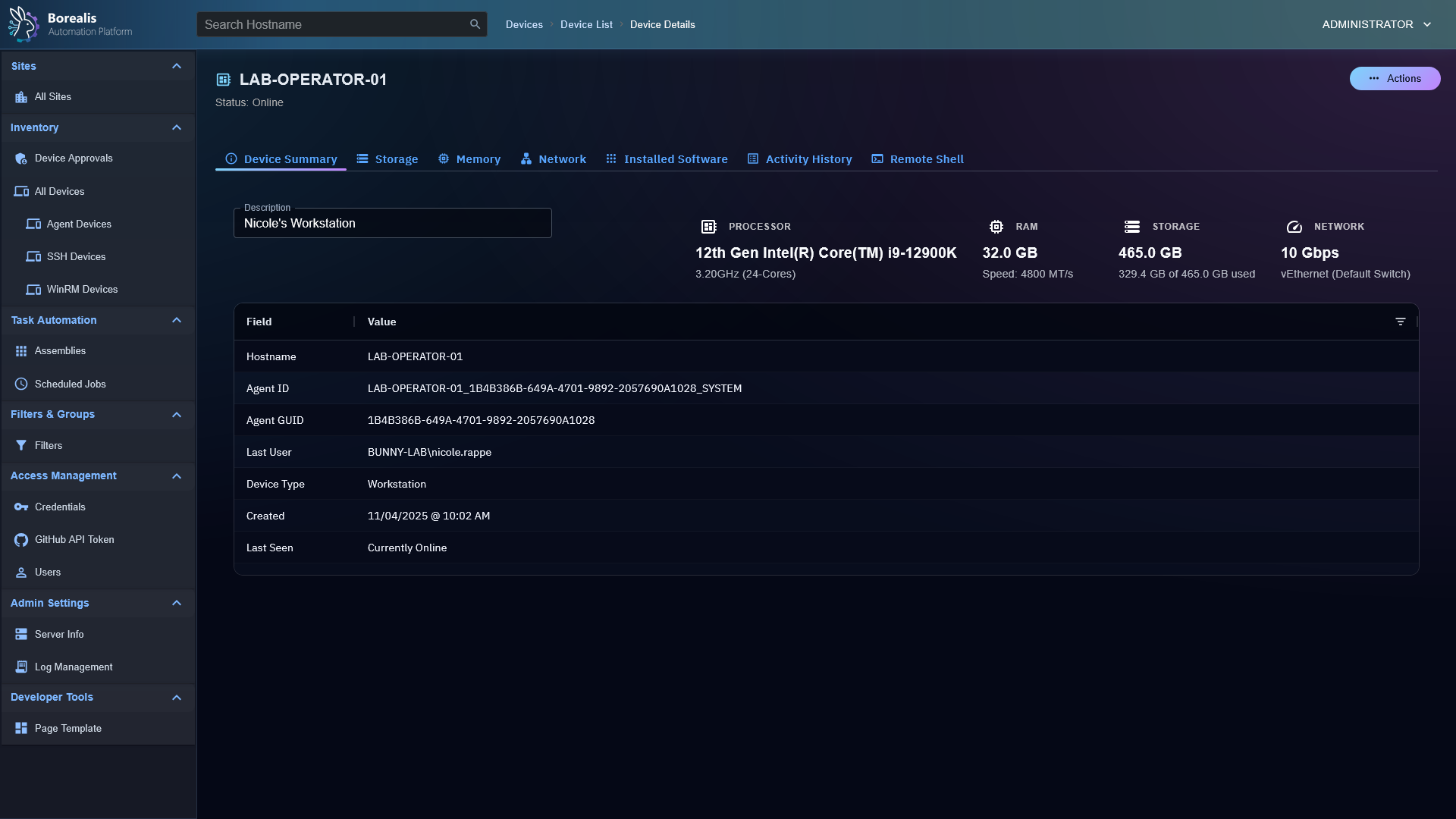
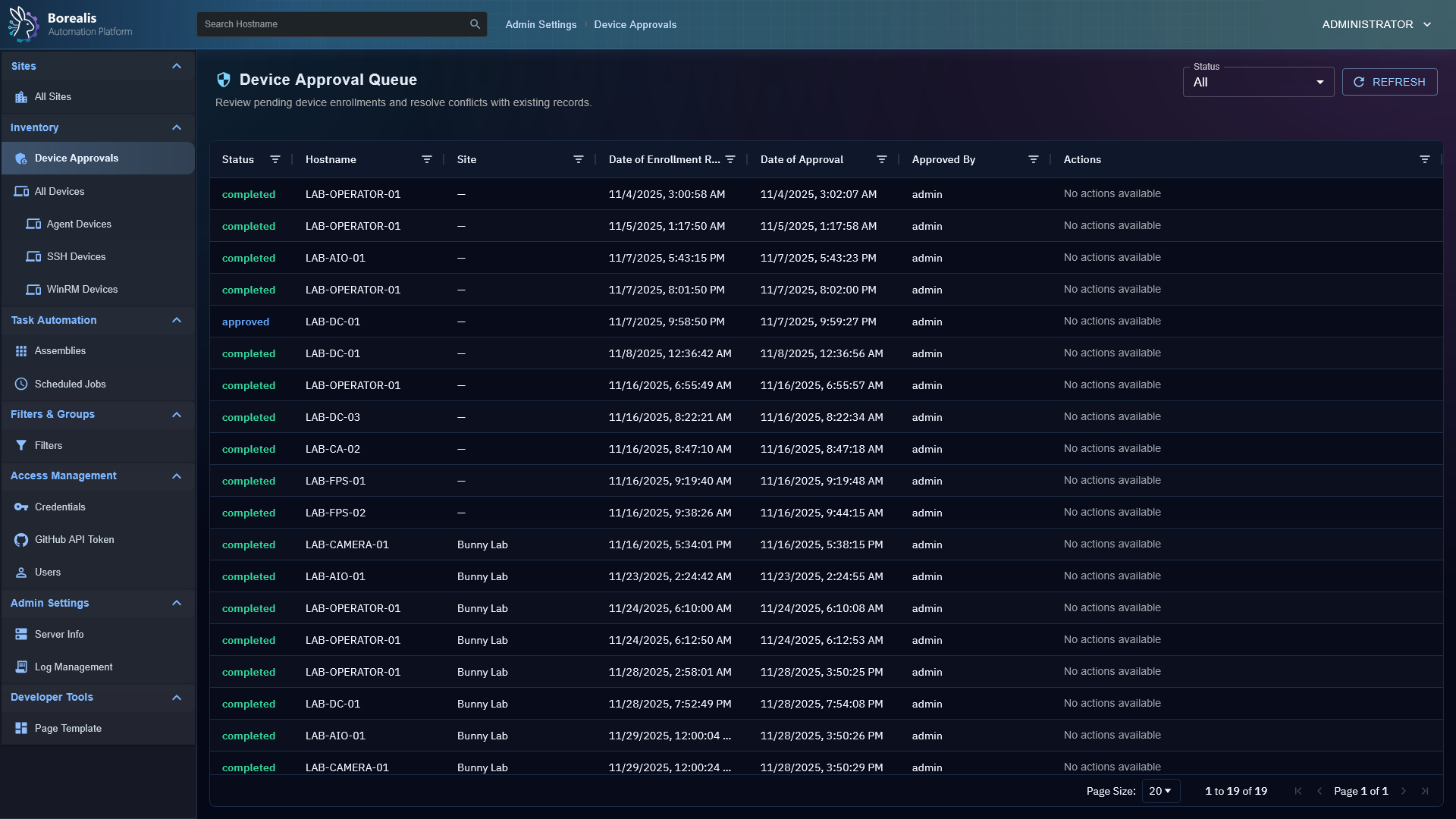
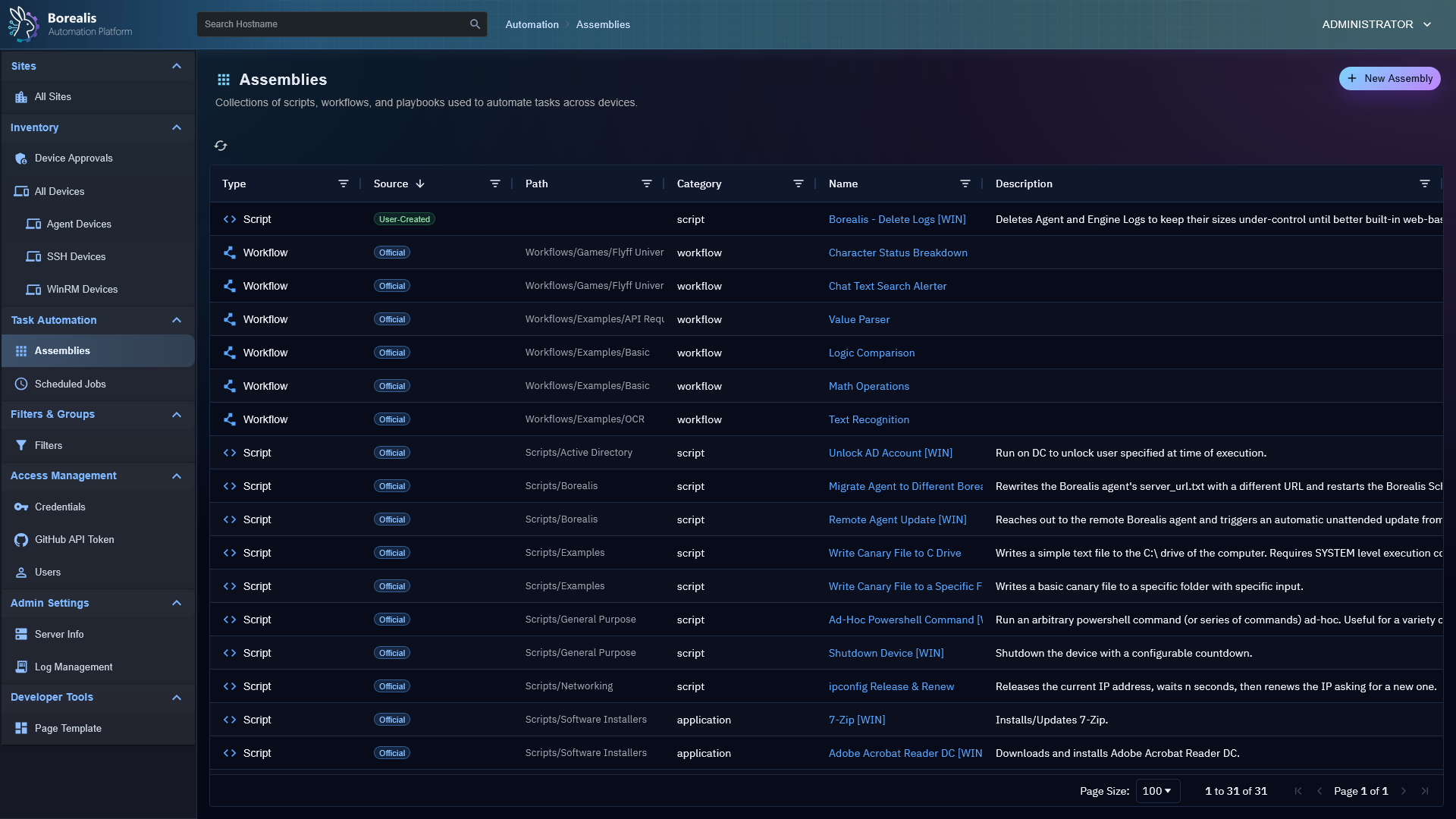
- Device Inventory: OS, hardware, and status posted on connect and periodically.
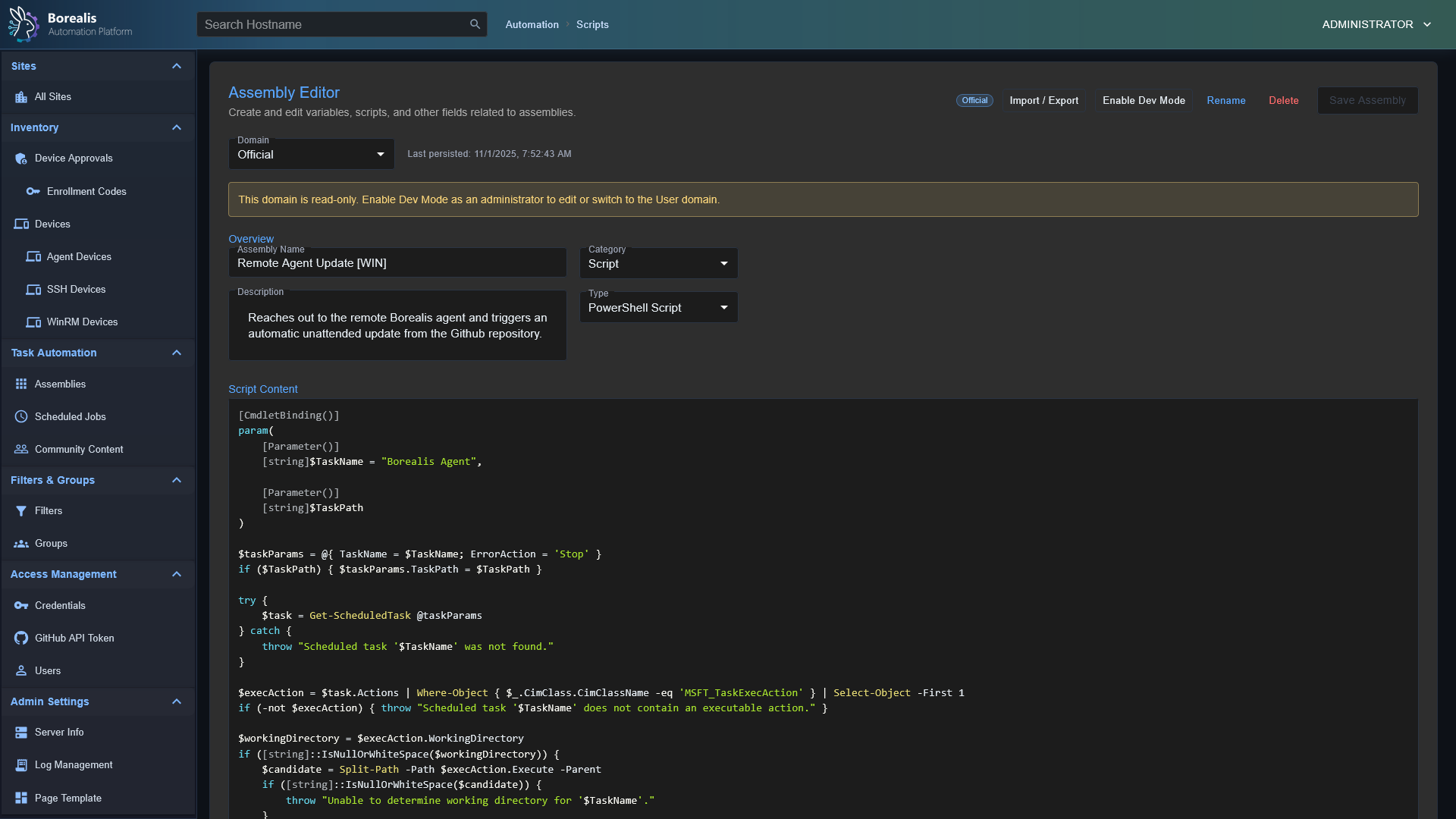
- Remote Script Execution: Run PowerShell in
CURRENT USERcontext or asNT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM. - Jobs and Scheduling: Launch "Quick Jobs" instantly or create more advanced schedules.
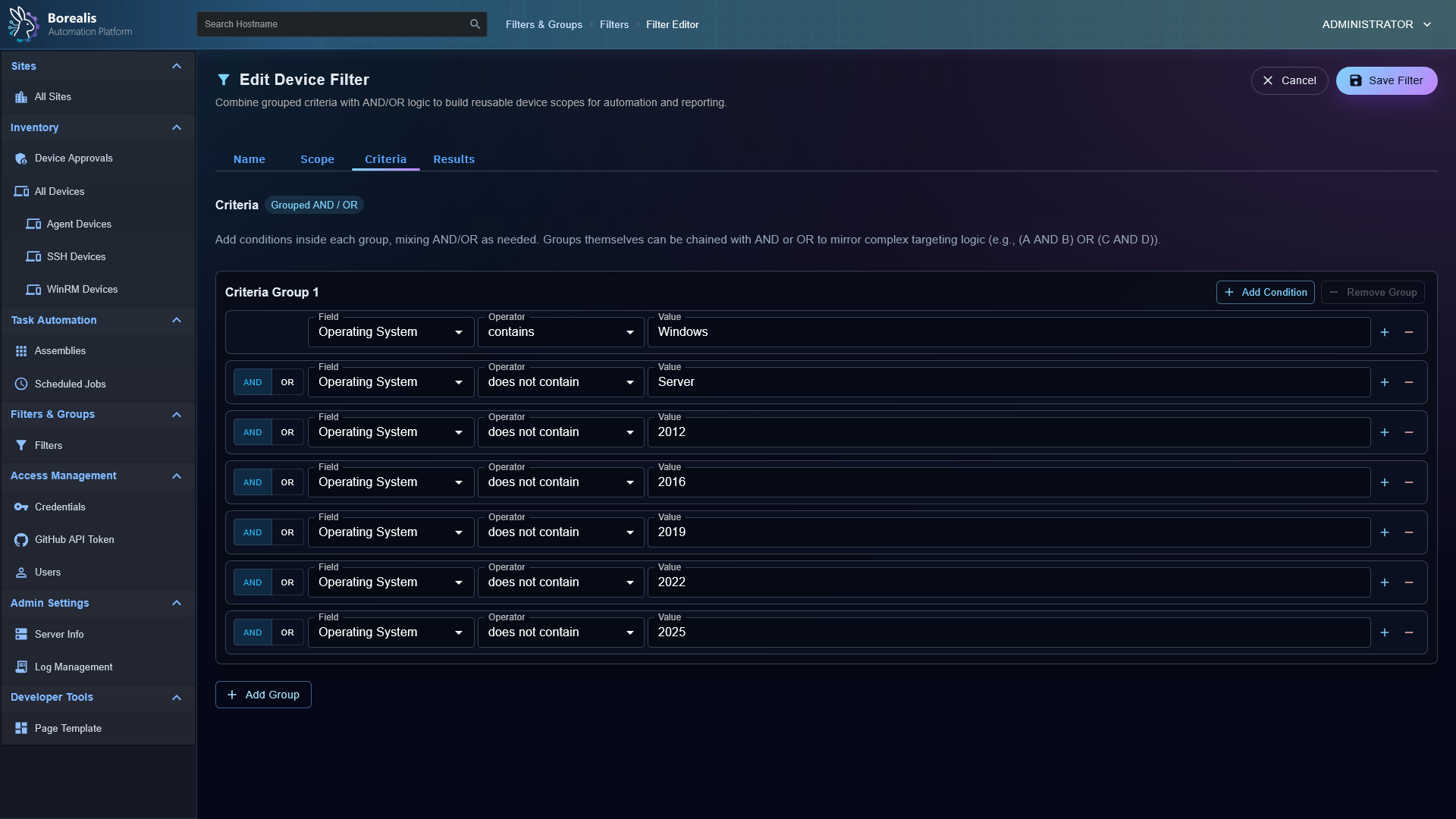
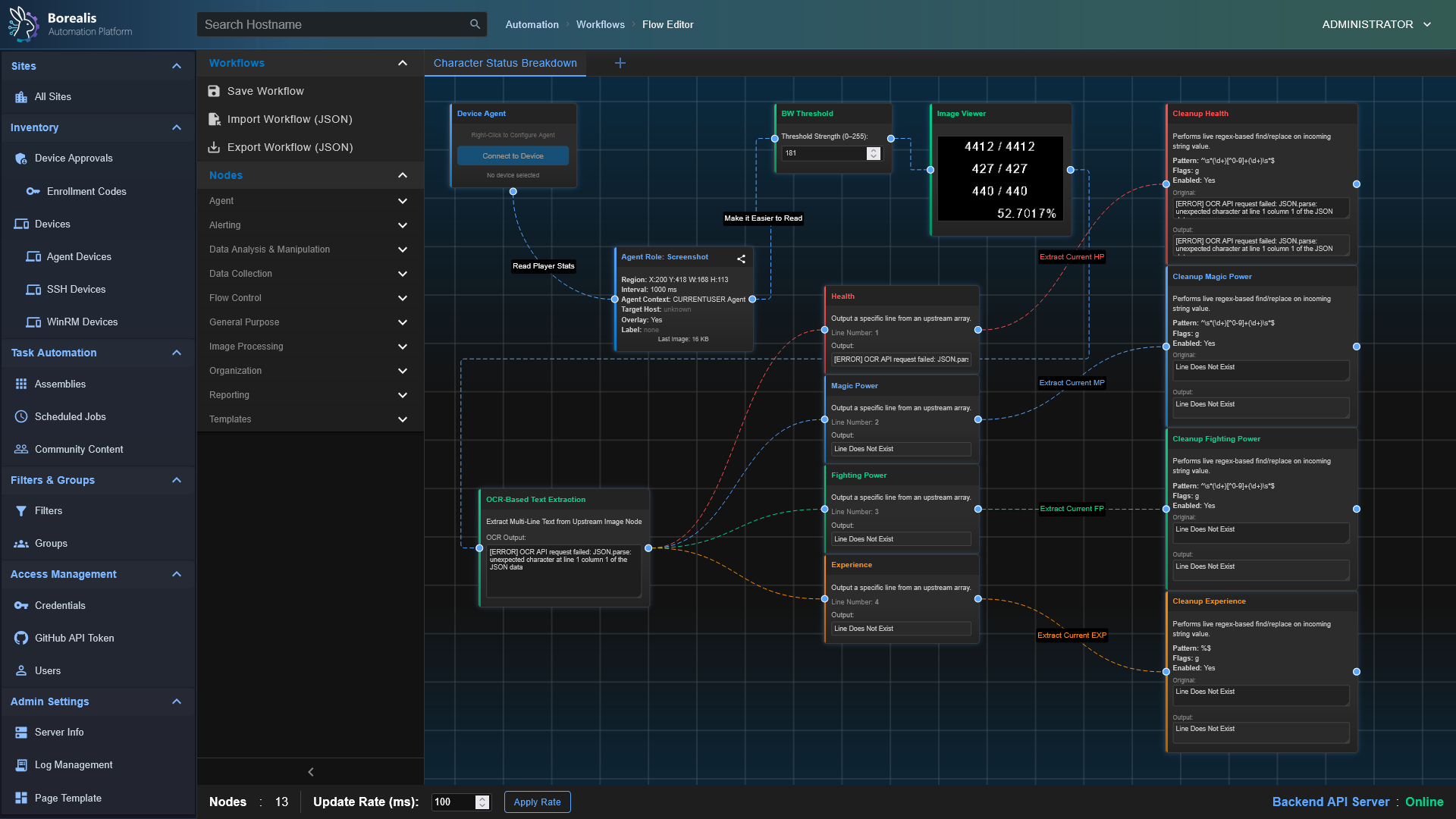
- Visual Workflows: Drag-and-drop node canvas for combining steps, analysis, and logic.
- Ansible Playbooks: Ansible playbook support is unfinished/broken in both the Engine and agent runtimes. The goal is to ship server-driven Ansible (SSH/WinRM) alongside agent-driven playbooks.
- Windows-first. Linux Engine support ships via
Borealis.sh(Engine is currently the focus); the Linux agent is not yet available; only settings can be staged - and the current Linux agent build would not execute scripts, audits, or likely even enroll reliably.
Current Status & Limitations
- Ansible is disabled/unstable: Engine quick-run returns not implemented, scheduled-job and agent paths are incomplete, and server-side SSH/WinRM playbook dispatch is still on the roadmap. Expect failures until the Ansible pipeline is rebuilt.
- Linux agent is non-functional: script execution, auditing, and enrollment flows are Windows-only right now. Avoid Linux agent deployments until a proper port is delivered. The core of Borealis is Python and Java, so it's already inherantly compatible with Linux, and you will find that the Engine runs fine in Linux, but the Agent needs a huge amount of work to account for various Linux distributions.
Device Management
Assembly Management
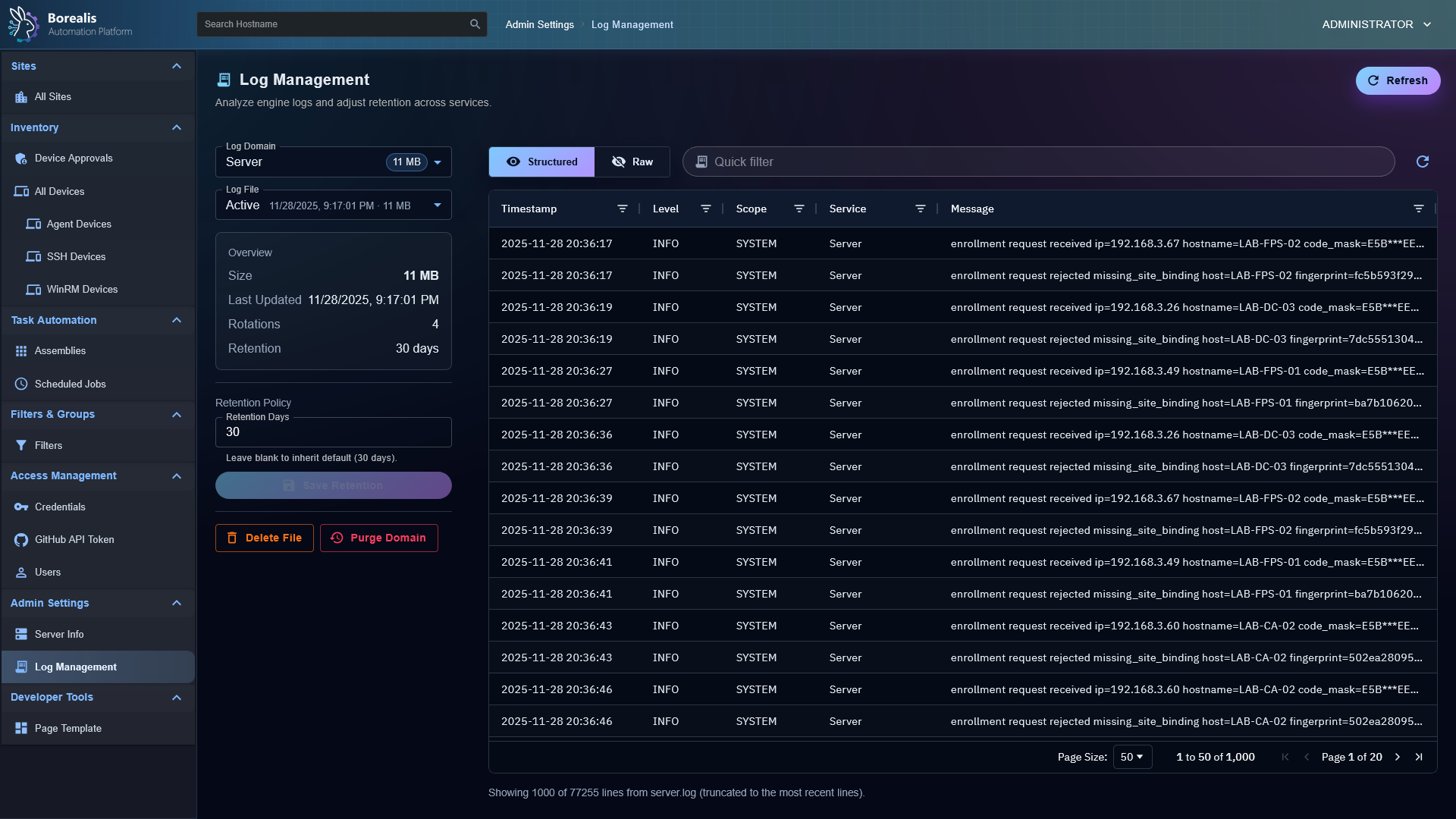
Log Management
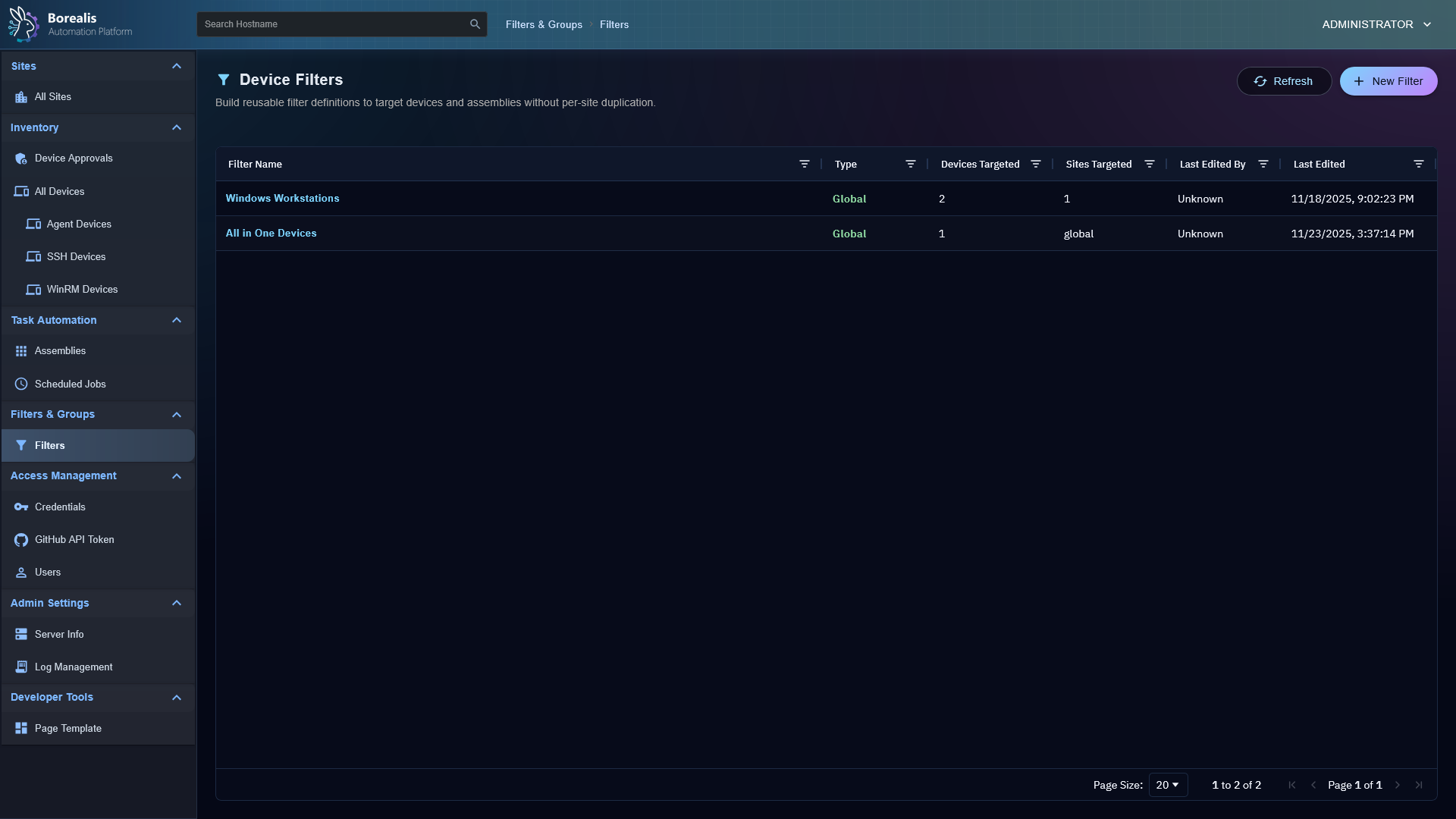
Misc Management Sections
Getting Started
Installation
- Start the Engine:
- Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -EngineProductionProduction Engine @ https://localhost:5000 - Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -EngineDevDev (Vite + Flask) @ https://localhost:5173 - Linux (Engine only):
./Borealis.sh --EngineProductionProduction Engine @ https://localhost:5000 (use--EngineDevfor Vite)
- Windows:
- (Optional) Install the Agent (Windows, elevated PowerShell):
- Windows:
./Borealis.ps1 -Agent - Linux agent binaries are not available yet;
Borealis.sh --Agentonly stages config settings.
- Windows:
Description
Languages
Python
48.8%
JavaScript
42.8%
PowerShell
7.3%
Shell
0.8%
CSS
0.2%
Other
0.1%